HPV primary screening and abnormal screen follow-up
- Downloads
- Full report (pdf)
Abnormal screen result follow-up
Follow-up on abnormal screen results varies across countries, but typically includes colposcopy, treatment, and post-treatment follow-up.
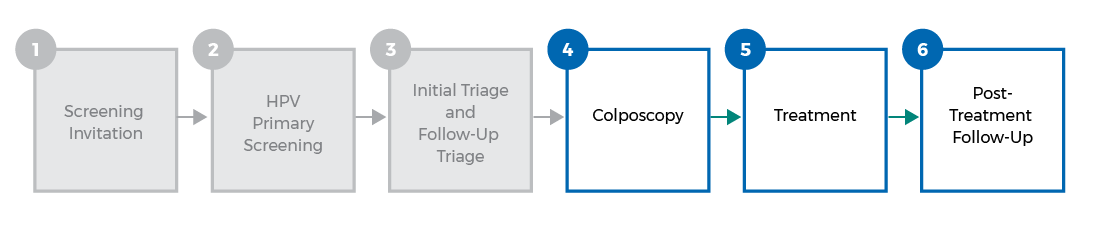
Colposcopy
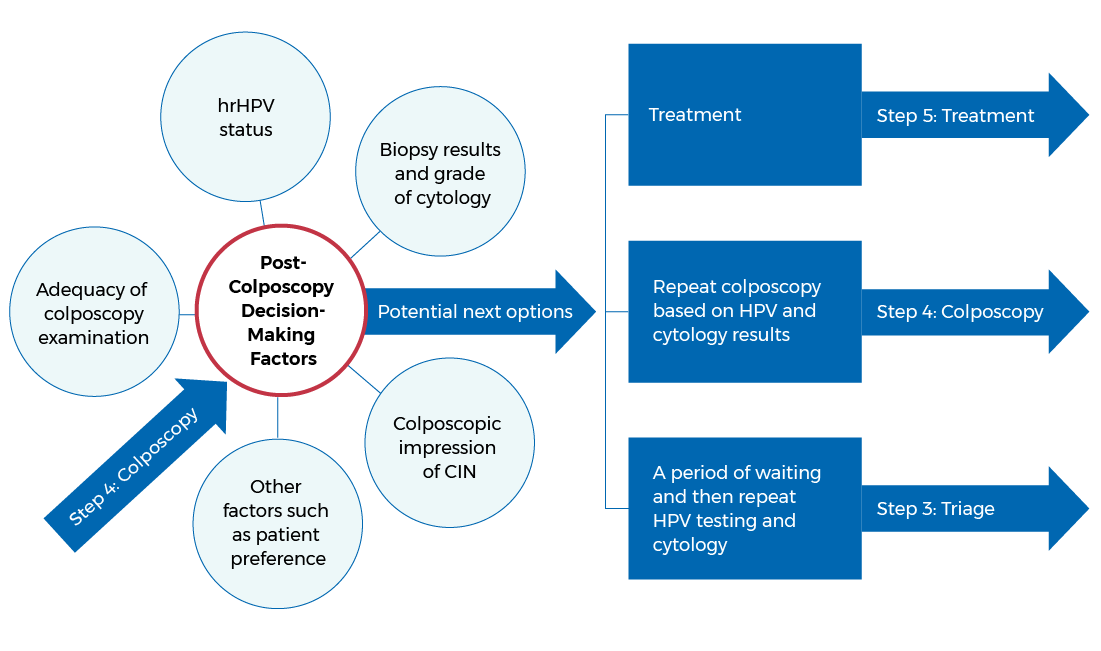
Individuals are referred to colposcopy based on the outcomes of the triage tests and procedures. Colposcopy is the main diagnostic procedure for cervical cancer and cancer precursors. Other countries use a variety of factors to determine what happens after colposcopy:
- Adequacy of the colposcopy examination
- High-risk HPV status
- Grade of cytology
- Biopsy results and impression of CIN
- Colposcopic impression of CIN
- Other variables, such as patient preference
After colposcopy, an individual may undergo:
- A period of waiting and repeat HPV testing with or without cytology
- Another colposcopy procedure
- Treatment
Overview of the factors that determine next steps after colposcopy
Treatment
Treatment options include loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), laser ablation, cryocautery, cone biopsy, and other excisions. More advanced cases may require hysterectomy, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Post-treatment follow-up
Post-treatment follow-up is needed to ensure the treatment was successful and typically includes:
- HPV testing
- Cytology
- Colposcopy
The United Kingdom uses HPV testing as the first step in post-treatment follow-up, while Australia uses co-testing with cytology. Cytology is usually recommended if an individual tests positive for HPV during post-treatment follow-up. The individual will return to routine screening after sufficient cycles of repeat HPV testing with negative results (the timelines and number of retesting cycles varies by country).
- Downloads
- Full report (pdf)
